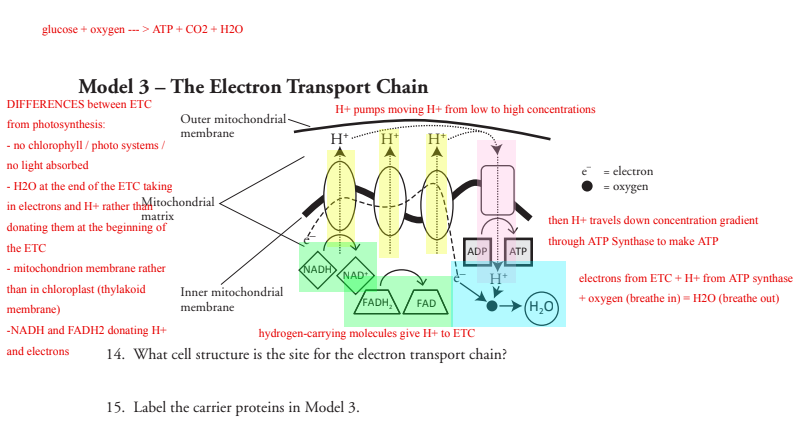
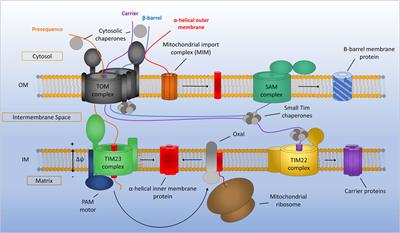
43 label the carrier proteins in model 3.
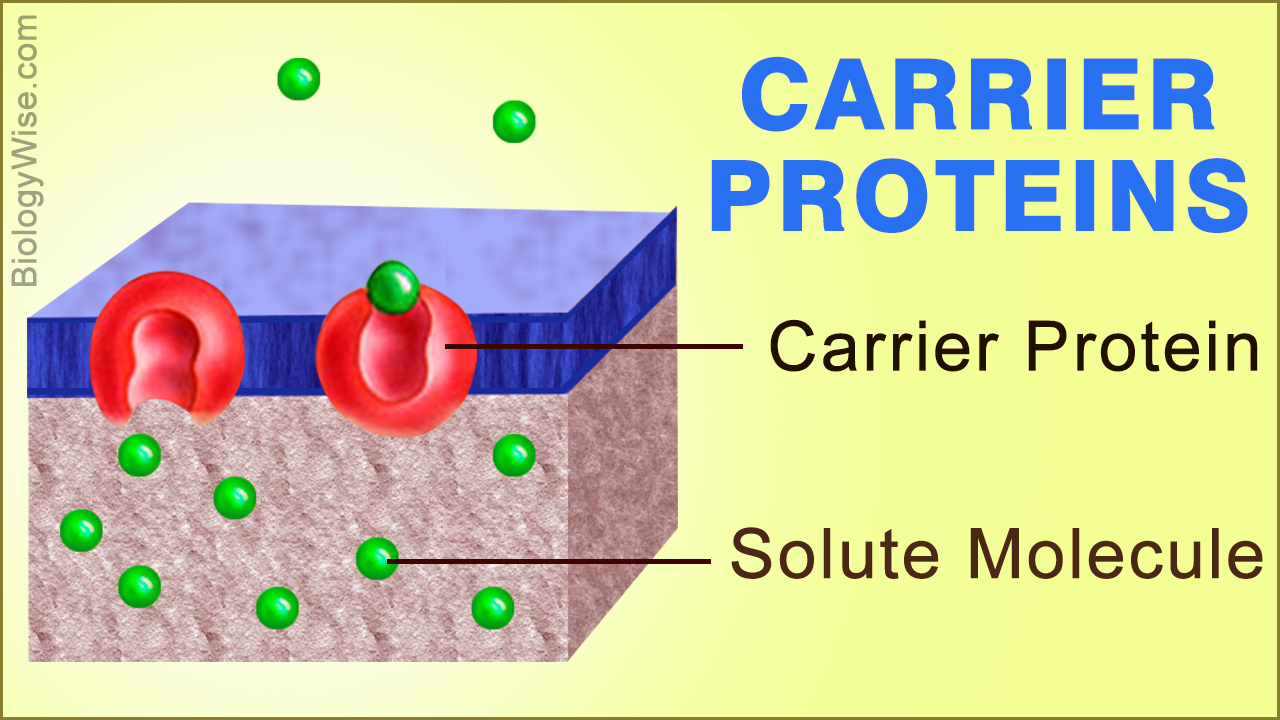
Carrier Proteins: Types & Functions - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Carrier proteins use a process called carrier mediated transport to assist molecules across the cell membrane. As stated earlier, the makeup of the amino acid chains in the protein... What are Carrier Proteins? - Study.com A carrier protein is a membrane protein that moves solutes across the membrane by creating conformational changes in the protein. The main carrier protein function is to move molecules...
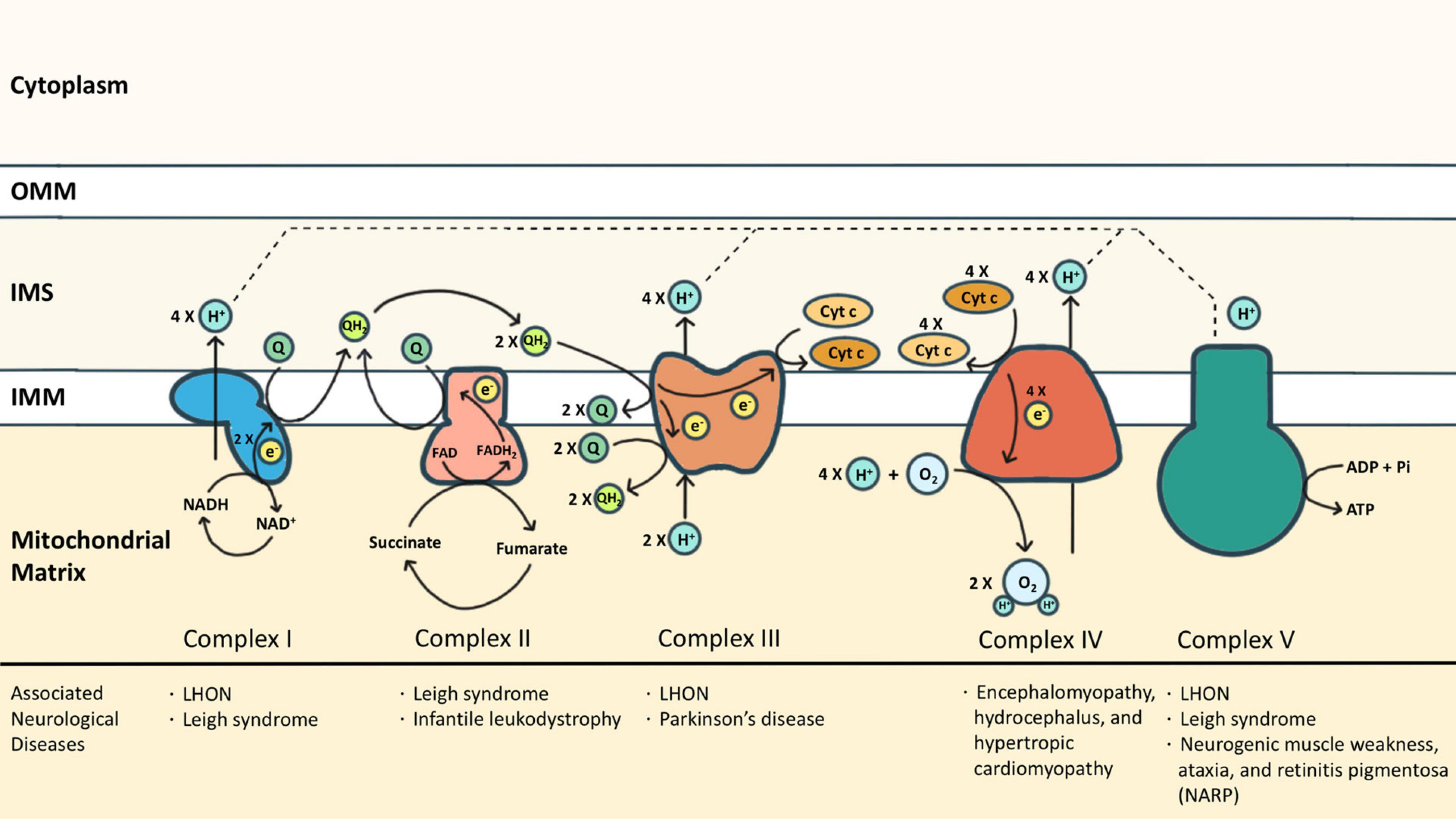
Solved Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain H Η' Η' cell - Chegg Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. (Which ones are the cytochromes?) 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the Question: Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain H Η' Η' cell wall dectron oxygen cell membrane ADP ATP NADH NAD FADH FAD (HO) 14. What cell structure is the site for the electron transport chain?

Label the carrier proteins in model 3.
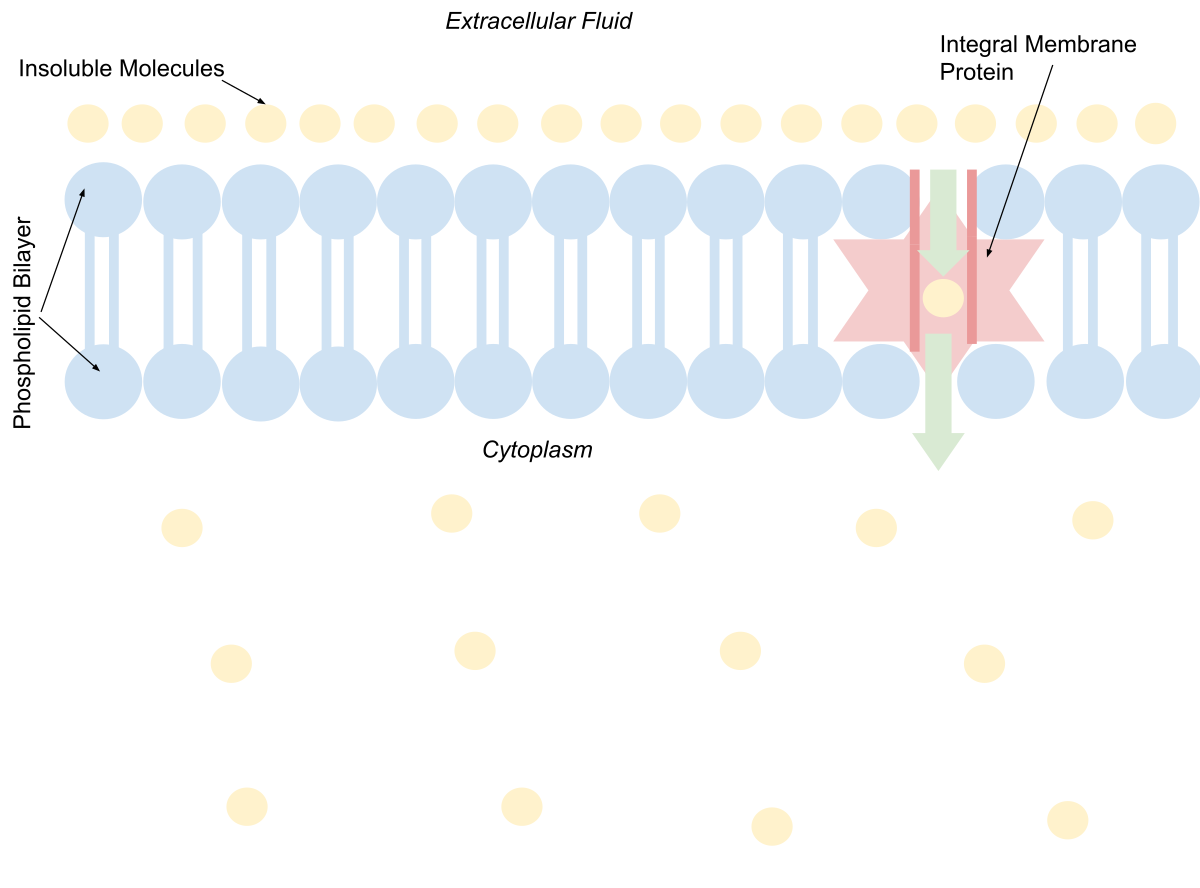
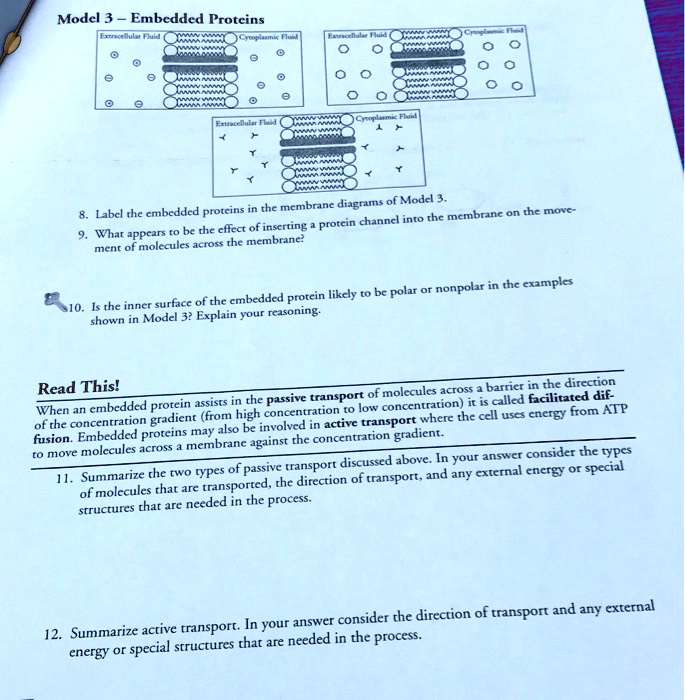
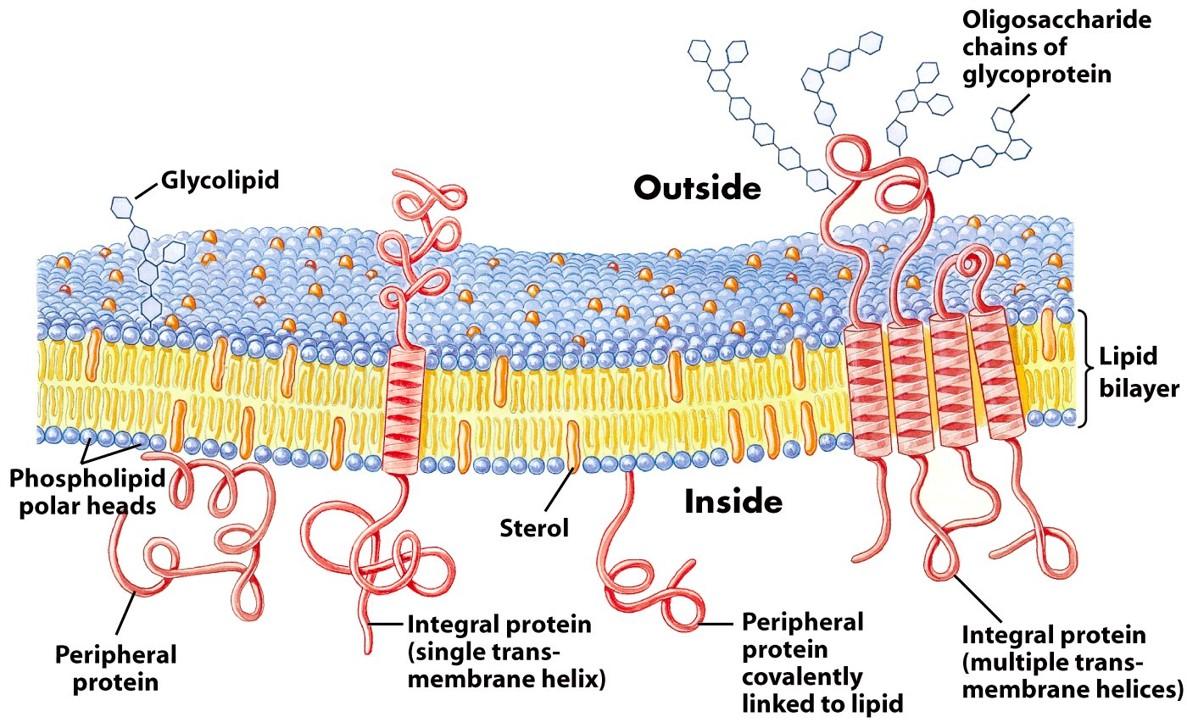
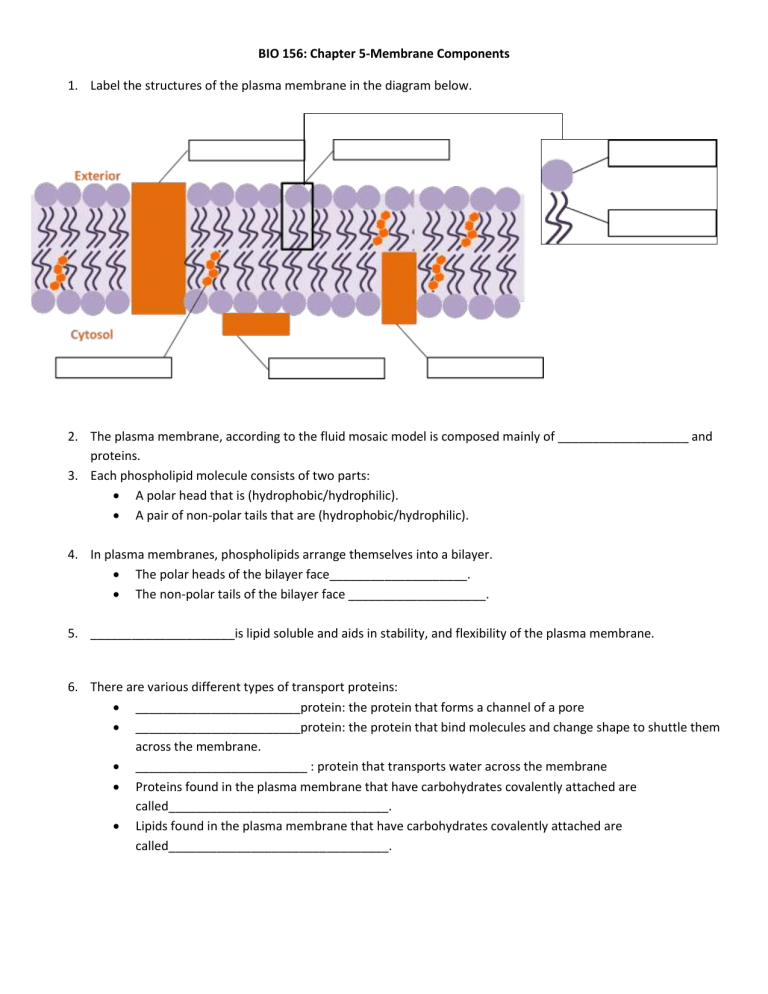
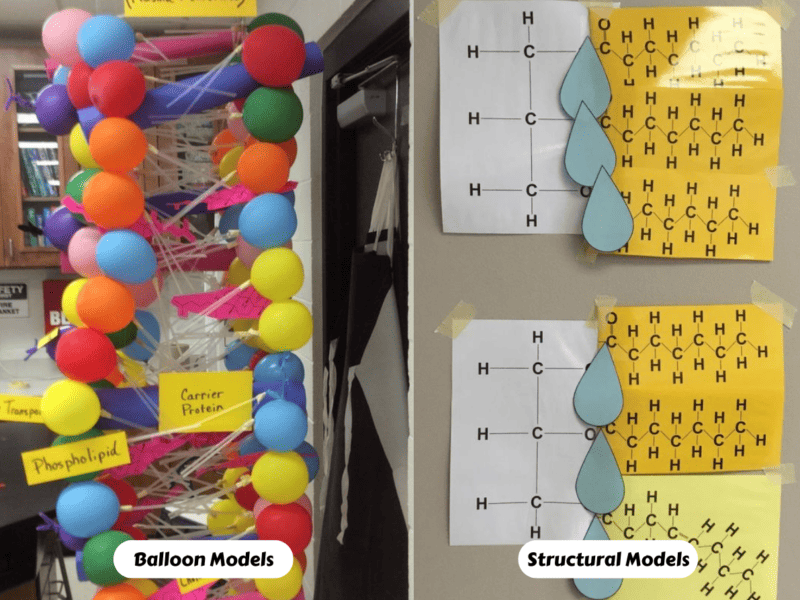
Channel Protein: Definition, Function, Examples - Biology Dictionary Channel Proteins and Carrier Proteins. There are four types of transport that occur within cells. Simple diffusion occurs with small gas molecules, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, as well as many non-polar chemicals such as steroid hormones and medicinal drugs. These molecules have the right chemistry and size to pass right through the cell ... Label - Wikipedia A label (as distinct from signage) is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed directly on a container or article can also be considered labelling . Plasma Membrane Structure - Function, Components, Structure, Fluid ... The model describes plasma membrane structure as a mosaic of components which includes proteins, cholesterol, phospholipids, and carbohydrates; it imparts a fluid character on the membrane. Thickness of the membrane is in the range of 5-10nm. The proportion of constituency of plasma membrane i.e., the carbohydrates, lipids and proteins vary ...
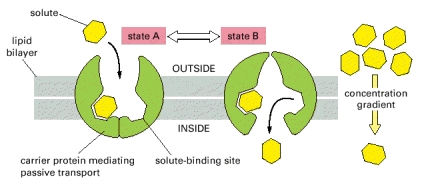
Label the carrier proteins in model 3.. Biology A: Unit 3 Flashcards | Quizlet What is the function of receptor proteins? to detect outside conditions and signal the information to the inside of the cell Which statement describes how molecules move when there is a concentration gradient? Molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration to restore equilibrium. Carrier Proteins and Active Membrane Transport This schematic diagram shows carrier proteins functioning as uniporters, symporters, and antiporters. The tight coupling between the transport of two solutes allows these carriers to harvest the energy stored in the electrochemical gradient of one solute, typically an ion, to transport the other. Create and Print Shipping Labels | UPS - United States Required Labels for Domestic Air. Your domestic shipments using air services require that you use a label printed from an automated shipping system (like UPS.com) or a UPS Air Shipping Document. The ASD combines your address label, tracking label and shipping record into one form. Specific ASDs are available for: HTML label tag - W3Schools Proper use of labels with the elements above will benefit: Screen reader users (will read out loud the label, when the user is focused on the element) Users who have difficulty clicking on very small regions (such as checkboxes) - because when a user clicks the text within the element, it toggles the input (this increases the hit area).
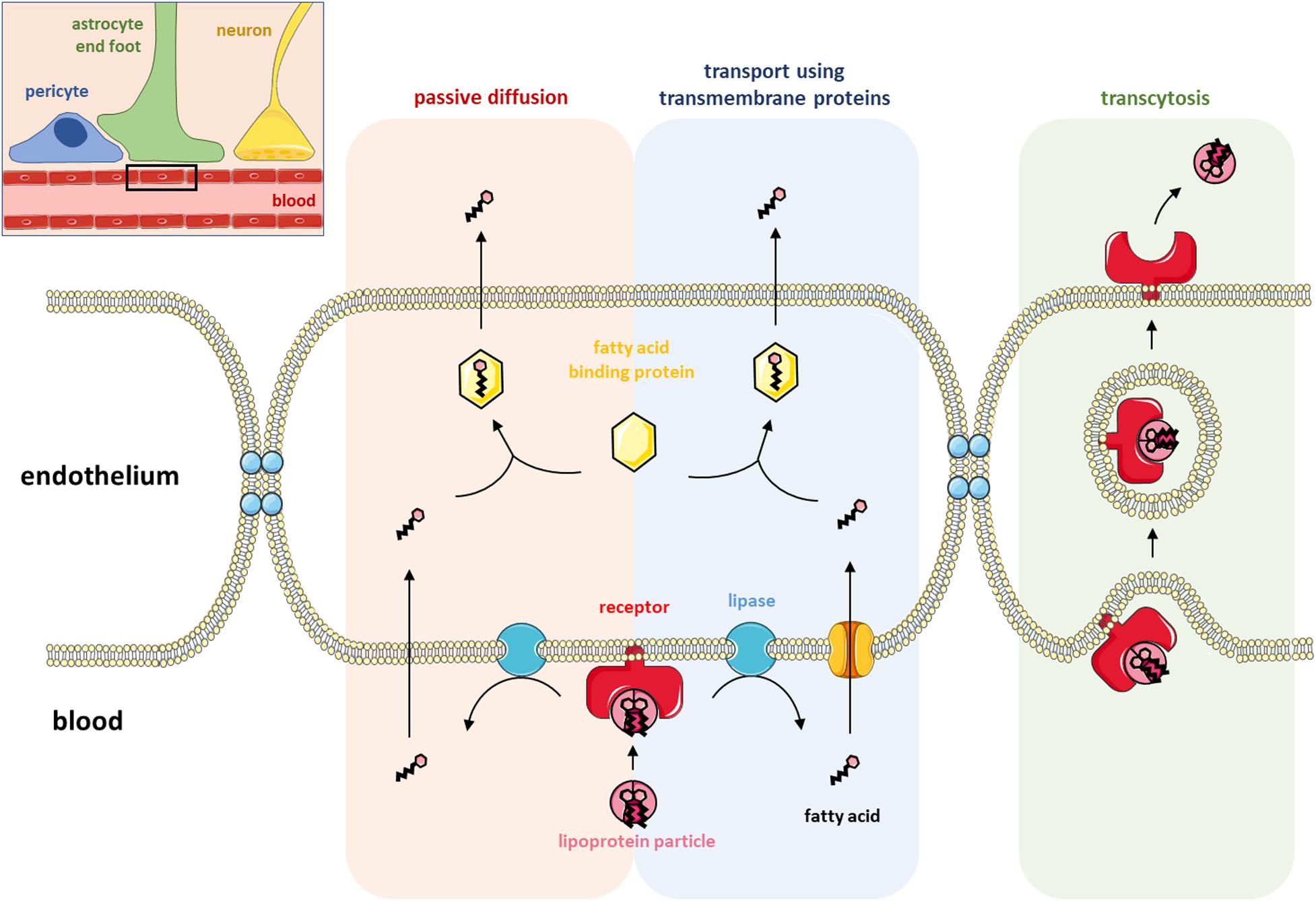
Cell membrane proteins (video) | Khan Academy Glycoprotein=sugar+protein. cell membrane or one can say plasma membrane is made up of lipids as well as proteins . The lipids or the head of lipid ( hydrophilic part) and the proteins which are on the surface of the cell membrane gets attached to sugars for cell signaling process and form glycolipid and glycoproteins. ( 5 votes) Upvote Downvote PDF Model 1 Glycolysis - psd202.org 15. Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? HYDROGEN IONS (H+) Read This! NADH and FADH 2 molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons. The result of these multiple processes is the How to Create and Print Labels in Word - How-To Geek Apr 12, 2019 · The “Label” section gives you a description of your current label selection. To change it, you’ll need to select “Options.” Let’s go ahead and do that. In the Label Options window, you can tell Word how you’ll be printing the labels and the brand of the label. Under “Product number,” you can select the label type from the provided list. The Role Of Channel And Carrier Proteins In Transporting Substances ... Carrier proteins are critical for the transport of molecules across biological membranes. Carriers are critical for chemical transport across the membrane in response to concentration gradient or when the phospholipid bilayer is impermeable to chemicals. Carrier proteins also function as a means of transporting other biological compounds.
3.1 The Cell Membrane - Anatomy & Physiology Figure 3.1.4 - Facilitated Diffusion: (a) Facilitated diffusion of substances crossing the cell (plasma) membrane takes place with the help of proteins such as channel proteins and carrier proteins. Channel proteins are less selective than carrier proteins, and usually mildly discriminate between their cargo based on size and charge. Free Label Printing Software - Avery Design & Print Avery Design & Print Online is so easy to use and has great ideas too for creating unique labels. I use the 5160 labels to create holiday labels for my association every year. We have over 160 members that we send cards to and all I have to do is use my Excel file of member names and import them into the my design that I created. Simple diffusion and passive transport (article) | Khan Academy Selective permeability is essential to cells' ability to obtain nutrients, eliminate wastes, and maintain a stable interior environment different than that of the surroundings (maintain homeostasis). The simplest forms of transport across a membrane are passive. Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a ... All Label Templates | Avery.com 3" x 2-1/4". White. Print to the Edge. Template. 2-1/2" diameter. Brown. Print to the Edge. Available in: Showing 1-12 of 517.
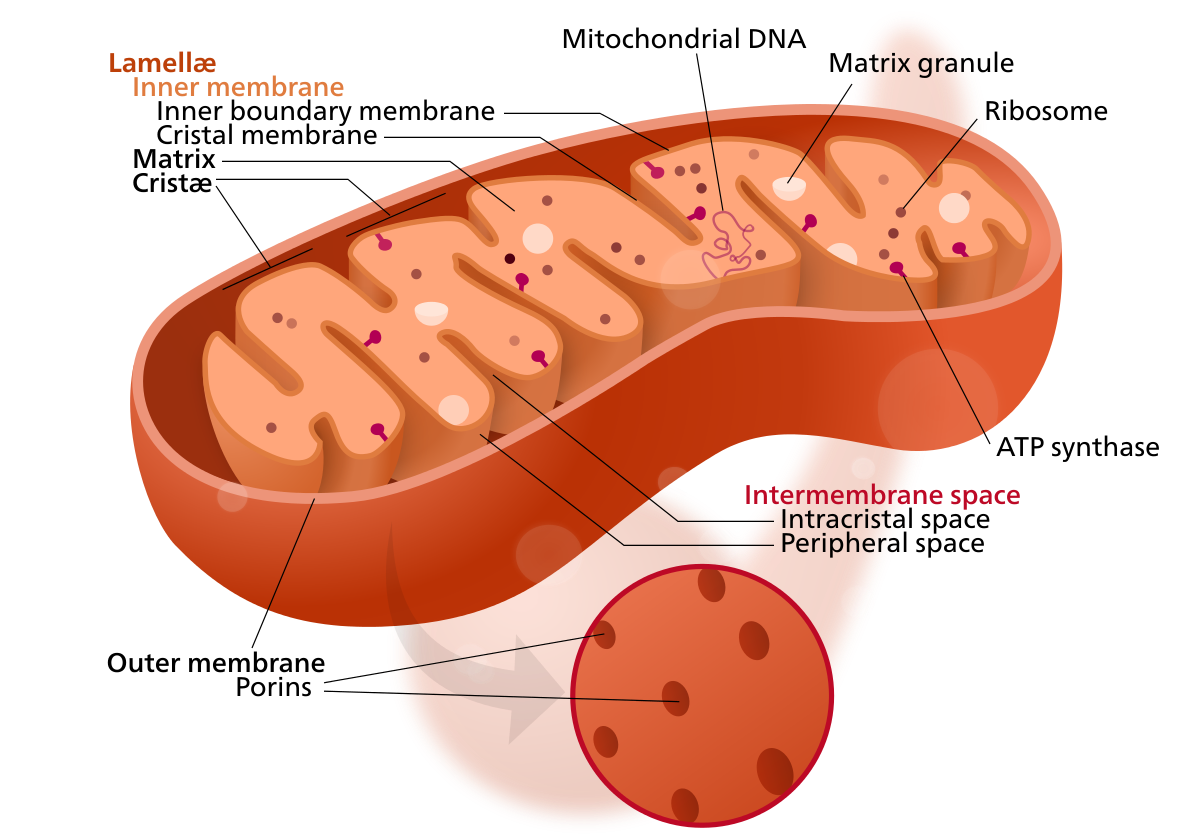
Biochemistry, Electron Transport Chain - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Complex III, also known as cytochrome c reductase, is made up of cytochrome b, Rieske subunits (containing two Fe-S clusters), and cytochrome c proteins. A cytochrome is a protein involved in electron transfer that contains a heme group. The heme groups alternate between ferrous (Fe2+) and ferric (Fe3+) states during the electron transfer.
Label - definition of label by The Free Dictionary label noun 1. An identifying or descriptive slip: tag, ticket. 2. A name or other device placed on merchandise to signify its ownership or manufacture: brand, colophon, mark, trademark. verb 1. To attach a ticket to: mark, tag, ticket. 2. To set off by or as if by a mark indicating ownership or manufacture: brand, identify, mark, tag, trademark. 3.
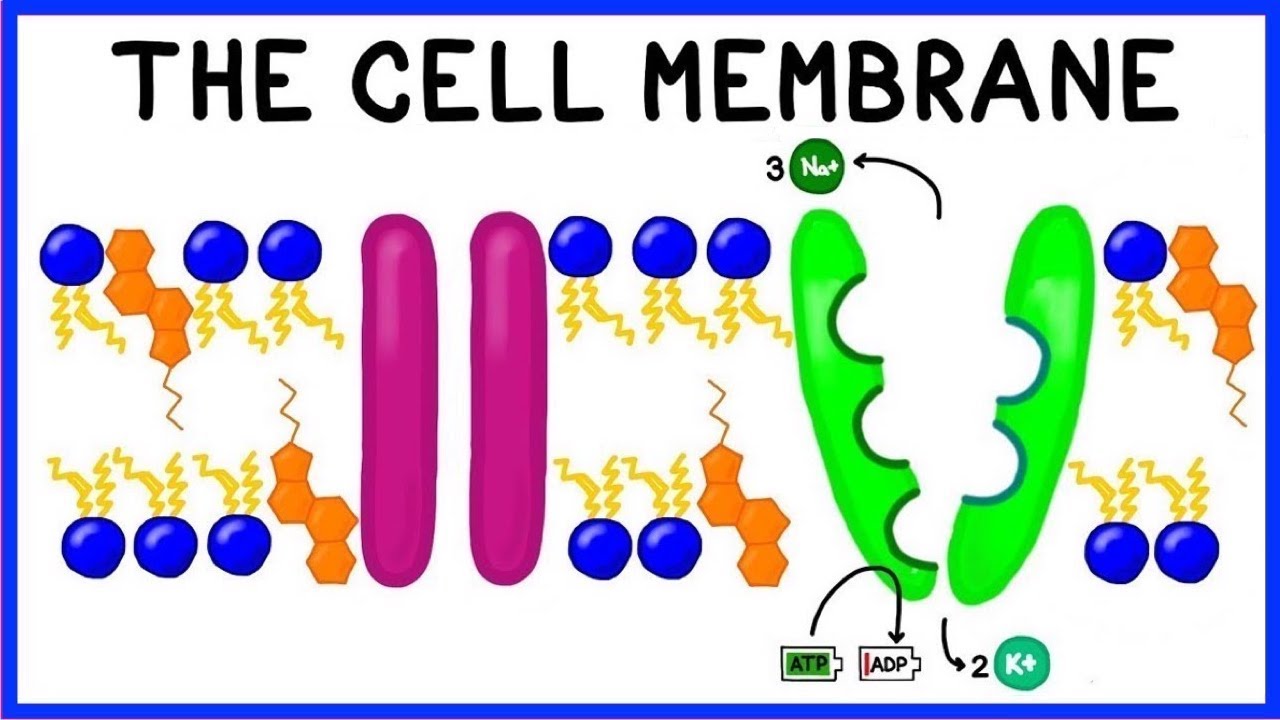
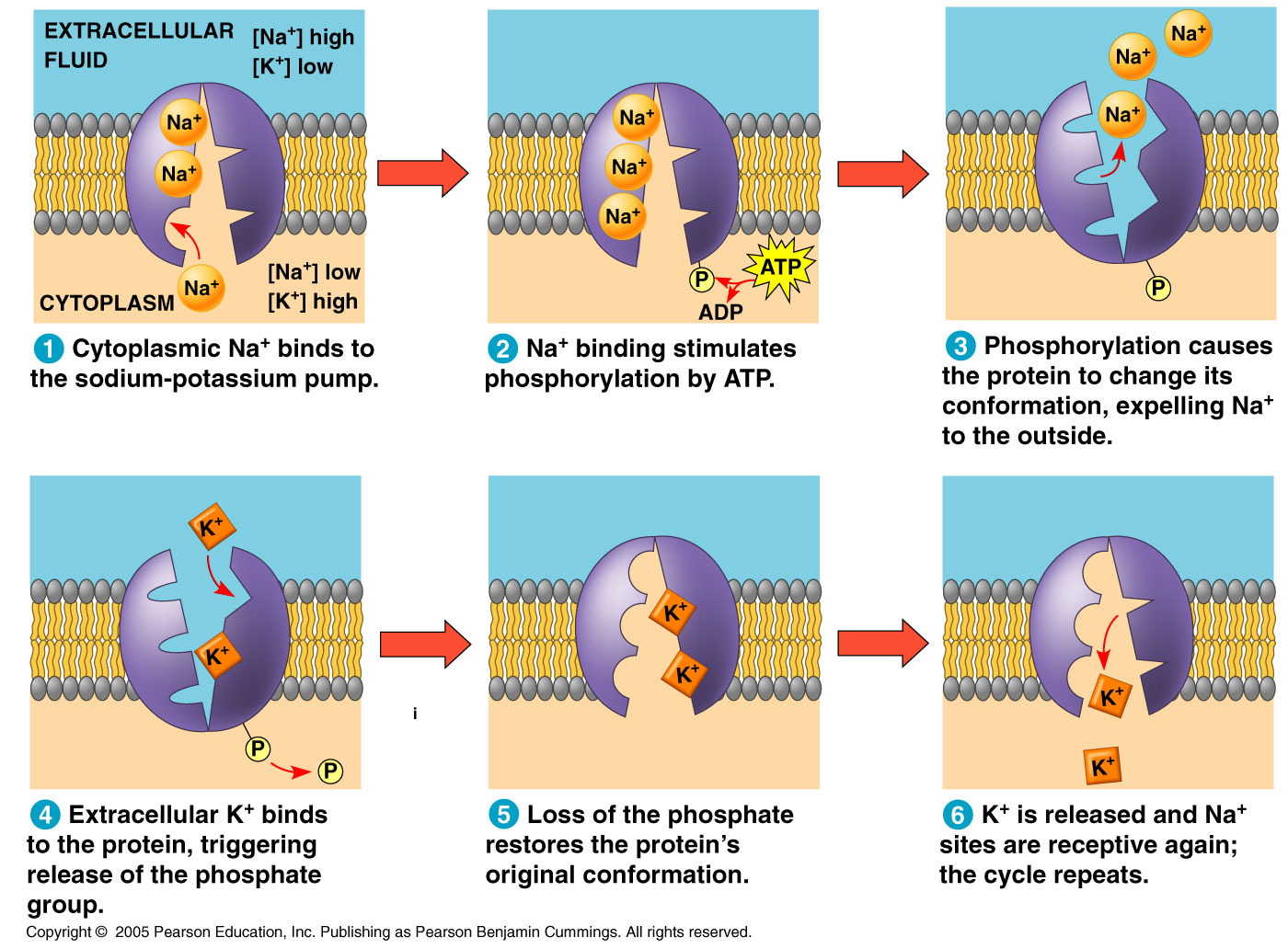
5.3 Active Transport - Biology for AP® Courses | OpenStax Connection for AP ® Courses. If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient, the cell must use free energy, often provided by ATP, and carrier proteins acting as pumps to move the substance. Substances that move across membranes by this mechanism, a process called active transport, include ions, such as Na + and K +.
5 Carrier Proteins Types (Example) and Function: Complete Guide! Carrier proteins that transport molecules against the concentration gradient are those that use substantial energy. ATP-driven carrier proteins are those requiring ATP to transport molecules whereas electrochemical potential-driven proteins are those fueled by electrochemical potential. Types of carrier proteins in passive transport
carrier protein Flashcards | Quizlet carrier protein. Proteins that change shape to allow a substance to pass through the plasma membrane. phagocytosis. the engulfing of food by a cell. facilitated diffusion. Facilitated Diffusiona passive form of carrier transport. exocytosis. the process by which wastes are packaged in vesicles and leave the cell. active transport.
Solved Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain Outer | Chegg.com Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the innet mitochondrial This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) 14.
2.14: Facilitated Diffusion - Biology LibreTexts Carrier proteins are involved in passive and active transport. A model of a channel protein and carrier proteins is shown in Figure below. Facilitated diffusion through the cell membrane. Channel proteins and carrier proteins are shown (but not a gated-channel protein). Water molecules and ions move through channel proteins.
13 Cellular Respiration-S - North Kitsap School District 15. Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? Read This! NADH and FADH 2 molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons. The result of these multiple processes is the production of large
Cellular Respiration.pdf - Cellular Respiration How is... Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? Read This! NADH and FADH2molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported across the innermitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons.
PDF Cellular Respiration - Welcome to Honors Biology 1 Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? Read This! NADH and FADH 2 molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons. The result of these multiple processes is the production of large
Carrier Protein - Definition, Function and Examples - Biology Dictionary Carrier Protein Definition Carrier proteins are proteins that carry substances from one side of a biological membrane to the other. Many carrier proteins are found in a cell's membrane, though they may also be found in the membranes of internal organelles such as the mitochondria, chloroplasts, nucleolus, and others.
13_Cellular_Respiration-S.pdf - M Abby Cellular Respiration... Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? Read This! NADH and FADH2 molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported across the inner mitochondrialmembrane with the help of electrons.
Carrier Proteins: Definition & Function | StudySmarter Carrier proteins allow polar molecules and ions that cannot easily pass through the cell membrane to enter and exit the cell. Because of the cell membrane's structure, polar molecules and ions cannot easily enter the cell. The cell membrane is made of phospholipids arranged into two layers making it a phospholipid bilayer.
The Cell Membrane | Anatomy and Physiology I - Lumen Learning The lipid bilayer forms the basis of the cell membrane, but it is peppered throughout with various proteins. Two different types of proteins that are commonly associated with the cell membrane are the integral proteins and peripheral protein (Figure 3). As its name suggests, an integral protein is a
DOCX Why? - Commack Schools Cellular Respiration. 5. Cellular Respiration. Cellular Respiration. 5. 5. POGIL™ Activities for High School Biology. 6. POGIL™ Activities for High School Biology
The Function Of Carrier Proteins In Transporting Molecules Across Cell ... Carrier proteins are specific for the type of molecule they transport. For example, there are carrier proteins that transport ions, such as sodium and potassium, across cell membranes. There are also carrier proteins that transport small molecules, such as glucose, across cell membranes. All carrier proteins extend across the cell membrane.
Carrier Proteins: Definition, Function, and Examples - Research Tweet A carrier protein is a type of protein in biology that transports a specific item across intracellular compartments, into the extracellular fluid, or between cells, as opposed to channel proteins, which are another form of membrane transport protein that transports molecules less selectively.
PDF PROTEINS: THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE - Stanford University ture and that the enzymatic activities of certain crystallized proteins were due to unknown entities associated with an inert protein carrier. In 1934, J.D. Bernal and Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin showed that a crystal of the protein pepsinyielded a discrete diffraction pattern when placed in an X-ray beam.
Plasma Membrane Structure - Function, Components, Structure, Fluid ... The model describes plasma membrane structure as a mosaic of components which includes proteins, cholesterol, phospholipids, and carbohydrates; it imparts a fluid character on the membrane. Thickness of the membrane is in the range of 5-10nm. The proportion of constituency of plasma membrane i.e., the carbohydrates, lipids and proteins vary ...
Label - Wikipedia A label (as distinct from signage) is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed directly on a container or article can also be considered labelling .
Channel Protein: Definition, Function, Examples - Biology Dictionary Channel Proteins and Carrier Proteins. There are four types of transport that occur within cells. Simple diffusion occurs with small gas molecules, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, as well as many non-polar chemicals such as steroid hormones and medicinal drugs. These molecules have the right chemistry and size to pass right through the cell ...




















Post a Comment for "43 label the carrier proteins in model 3."